
In “Building strength and combating muscle weakness in older individuals: The power of resistance training,” you will discover the importance of resistance training in counteracting age-related muscle loss, known as sarcopenia, in older individuals. With a focus on men over 50, this article highlights the necessity of strength training to combat muscle wastage and physical frailty. Safety, recovery, and consistency are emphasized in these training routines, along with the inclusion of bodybuilding-style isolation exercises for optimal results. Additionally, the importance of cardiovascular health and the need for regular cardio and strength training to maintain muscle strength are discussed. Whether you are a beginner or have experience, this article provides different training plans and highlights the significance of basic movement drills and flexibility exercises. Don’t miss the ten exercises recommended for men over 50, including landmine shoulder press, trap bar deadlifts, gymnastic ring push-ups, walking lunges, chest supported rows, farmers carries, and goblet squats. Get ready to build strength and stay active at any age!
Age-related muscle loss and its impact
Age-related muscle loss, known as sarcopenia, is a natural process that occurs as we get older. It is characterized by a gradual decrease in muscle mass and strength, and can have a significant impact on the overall health and functionality of older individuals. Sarcopenia can lead to physical frailty, increased risk of falls and injuries, and a decline in overall quality of life.
Understanding sarcopenia
Sarcopenia is a complex condition that is influenced by various factors, including hormonal changes, decreased physical activity, and inadequate nutrition. As we age, our body’s ability to produce and utilize proteins decreases, leading to muscle breakdown and a decrease in muscle mass. This process is exacerbated by a sedentary lifestyle and a lack of regular exercise.
The consequences of muscle weakness in older individuals
Muscle weakness in older individuals can have a number of negative consequences. It can lead to a loss of mobility and independence, making it difficult for individuals to perform everyday tasks such as walking, climbing stairs, or carrying groceries. Muscle weakness also increases the risk of falls, which can result in serious injuries such as fractures or head trauma. Additionally, muscle weakness can contribute to a decrease in metabolism, making it harder for older individuals to maintain a healthy weight and body composition.
The benefits of resistance training
Resistance training, also known as strength training or weightlifting, has been shown to be highly effective in counteracting muscle weakness and physical frailty in older people. By challenging the muscles through resistance exercises, individuals are able to stimulate muscle growth and increase strength.
Counteracting muscle weakness and frailty
Resistance training is particularly effective in combating muscle weakness and frailty in older individuals. By engaging in regular strength training exercises, older individuals can increase muscle mass and improve muscle strength, ultimately improving their ability to perform daily activities and reducing their risk of falls and injuries. Strength training also helps to maintain bone density, reducing the risk of osteoporosis and fractures.
Improving overall health and functionality
In addition to its impact on muscle strength, resistance training has numerous other benefits for older individuals. It can improve cardiovascular health, increase metabolism, and enhance overall functionality and quality of life. Strength training has been shown to improve balance and coordination, which can help to prevent falls. It also strengthens connective tissues, such as tendons and ligaments, reducing the risk of joint injuries. Resistance training has even been shown to have positive effects on cognitive function and mental health, reducing the risk of age-related cognitive decline and depression.

The significance of strength training for men over 50
Strength training is especially important for men over 50, as they are particularly susceptible to muscle wastage and other age-related changes in muscle composition. As men age, their levels of testosterone, a hormone that helps to build and maintain muscle, naturally decline. This decline in testosterone can lead to a decrease in muscle mass and strength if not counteracted through regular strength training exercises.
Addressing muscle wastage
Strength training is crucial for men over 50 as it helps to address muscle wastage that occurs with age. By engaging in regular resistance exercises, men can stimulate muscle growth and maintenance, counterbalancing the natural decline in muscle mass. Strength training exercises that target major muscle groups, such as the chest, back, legs, and arms, are particularly effective in building muscle and increasing strength.
Maintaining independence and quality of life
Maintaining muscle strength and functionality is essential for men over 50 to maintain their independence and quality of life. By engaging in strength training, men can improve their ability to perform daily tasks, such as carrying groceries, lifting objects, and climbing stairs. This can help to prevent the loss of independence and ensure a higher quality of life as they age. Additionally, strength training has been shown to improve bone density, reducing the risk of osteoporosis and fractures in older men.
Key considerations in strength training for older individuals
While strength training is beneficial for older individuals, there are some important considerations to keep in mind to ensure safety and maximize results.
Safety precautions and guidelines
Safety should always be a top priority when engaging in strength training, especially for older individuals. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional or certified personal trainer before starting a new exercise program, especially if you have any underlying health conditions or are new to strength training. They can provide guidance on proper form, appropriate exercise selection, and any modifications that may be needed to accommodate individual needs or limitations.
Importance of proper recovery
Recovery is a crucial component of any strength training program, especially for older individuals. Giving your muscles time to rest and recover between workouts is essential for muscle growth and injury prevention. It is important to listen to your body and not overdo it, as pushing too hard can lead to overuse injuries or muscle strain. Adequate sleep, proper nutrition, and hydration are also important factors in supporting recovery and optimizing results.
Consistency and adherence to training programs
Consistency is key when it comes to strength training for older individuals. It is important to establish a regular exercise routine and stick to it in order to see progress and maintain results. Consistency also helps to build good habits and ensure that strength training becomes a sustainable part of a healthy lifestyle. Finding an exercise program or routine that you enjoy and that fits your schedule and preferences can help to increase adherence and make strength training a lifelong practice.

Incorporating isolation exercises into weightlifting routines
While compound exercises that target multiple muscle groups are effective for overall strength and functionality, incorporating isolation exercises into weightlifting routines can provide additional benefits, especially for men over 50.
Understanding the benefits of isolation exercises
Isolation exercises target specific muscles or muscle groups, allowing for a more targeted approach to muscle development and strength-building. By isolating individual muscles, you can focus on improving muscle imbalances, addressing weak areas, and improving overall muscle definition and aesthetics. Isolation exercises also help to improve joint stability, increase range of motion, and prevent muscle imbalances that can lead to injury.
Examples of effective isolation exercises for men over 50
There are numerous isolation exercises that can be incorporated into weightlifting routines for men over 50. Some examples include:
-
Bicep curls: This exercise targets the biceps brachii muscles, located in the front of the upper arm. By performing bicep curls with dumbbells or a barbell, you can effectively strengthen and develop these muscles.
-
Tricep kickbacks: This exercise targets the triceps brachii muscles, located in the back of the upper arm. By performing tricep kickbacks with dumbbells or resistance bands, you can effectively strengthen and tone these muscles.
-
Leg extensions: This exercise targets the quadriceps muscles, located in the front of the thighs. By performing leg extensions on a leg extension machine or with resistance bands, you can effectively strengthen and develop these muscles.
-
Calf raises: This exercise targets the calf muscles, located in the back of the lower leg. By performing calf raises on a calf raise machine or by using a step or elevated surface, you can effectively strengthen and tone these muscles.
It is important to always use proper form and start with a weight or resistance level that is appropriate for your fitness level. Gradually increase the weight or resistance as you become stronger to continually challenge your muscles and make progress.
The role of cardiovascular health in men over 50
As men age, the importance of cardiovascular health becomes increasingly significant. Cardiovascular exercise, also known as cardio or aerobic exercise, refers to activities that increase the heart rate and improve the efficiency of the cardiovascular system.
Increasing importance due to aging
Cardiovascular health is particularly important for men over 50 as they are more prone to cardiovascular diseases such as heart disease, high blood pressure, and stroke. Additionally, age-related changes such as a decrease in lung capacity and a decline in overall fitness make it even more crucial to maintain a healthy cardiovascular system.
Benefits of regular cardiovascular exercise
Regular cardiovascular exercise has numerous benefits for men over 50. It helps to improve heart health by strengthening the heart muscle and improving its ability to pump blood efficiently. Cardiovascular exercise also helps to lower blood pressure, reduce LDL cholesterol (commonly known as “bad” cholesterol), and improve blood circulation. It can also aid in weight management, increase energy levels, improve sleep quality, and reduce the risk of chronic diseases such as diabetes and certain types of cancer.

The importance of combined cardio and strength training
While both cardiovascular exercise and strength training offer their own unique benefits, combining the two is highly advantageous for older individuals, including men over 50.
Maintaining muscle strength and functionality
Combining cardio and strength training in a balanced exercise program helps to maintain muscle strength and functionality. While strength training builds muscle mass and strength, cardiovascular exercise helps to improve endurance, stamina, and cardiovascular fitness. This combination is essential for maintaining overall functional fitness and independence as we age. For example, having strong muscles is important for carrying groceries or lifting objects, while good cardiovascular fitness is necessary for activities such as walking or climbing stairs without becoming fatigued.
Enhancing overall fitness and well-being
Combining cardio and strength training also enhances overall fitness and well-being in older individuals. Cardiovascular exercise helps to improve lung capacity, respiratory function, and the overall efficiency of the cardiovascular system. Strength training, on the other hand, increases muscle mass, bone density, and metabolism. This combination can lead to improved body composition, increased energy levels, and a higher quality of life.
It is important to create a balanced exercise program that incorporates both cardiovascular and strength training exercises. This can be achieved by alternating between cardio and strength training workouts throughout the week, or by engaging in activities that combine both elements, such as circuit training or high-intensity interval training (HIIT).
Tailoring training plans based on experience level
When it comes to strength training, it is important to tailor training plans based on the individual’s experience level. This ensures that exercises and routines are appropriate for their current fitness level and helps to prevent injuries and overexertion.
Customizing routines for beginners, intermediate, and advanced individuals
For beginners, it is important to start with simple exercises that focus on fundamental movements and proper form. This helps to build a solid foundation of strength and mobility, and reduces the risk of injury. As beginners progress, they can gradually increase the intensity and complexity of their workouts by adding more weight, performing more sets and repetitions, or incorporating advanced exercise variations.
Intermediate individuals have a solid understanding of basic exercises and proper form, and can begin to incorporate more advanced exercises and training techniques into their routines. This can include exercises that target specific muscle groups or involve more complex movement patterns. Intermediate individuals can also focus on increasing the weight or resistance used in their workouts to continue challenging their muscles.
Advanced individuals have a higher level of strength and fitness and can handle more advanced exercises and training methods. They can incorporate advanced strength training techniques such as supersets, drop sets, or pyramids into their routines to further challenge their muscles. Advanced individuals can also focus on fine-tuning their exercise form and technique, as well as prioritizing progressive overload to continue making gains in strength and muscle development.
Regardless of experience level, it is important to continuously monitor progress and make adjustments to training plans as needed. This ensures ongoing progress and prevents plateaus.
Progressive overload and periodization
Progressive overload is a key principle in strength training that involves gradually increasing the demands placed on the muscles in order to continually stimulate growth and improvement. This can be achieved by increasing the weight or resistance used, performing more sets or repetitions, or decreasing rest periods between sets. By progressively overloading the muscles, individuals can continue to make strength and muscle gains over time.
Periodization is another important aspect of tailored training plans. It involves dividing a training program into different phases or cycles, each with its own specific goals and focus. This helps to prevent overtraining and burnout, as well as ensure ongoing progress and prevent plateaus. Periodization can include different training intensities, volume, and exercises. It is important to work with a qualified fitness professional or personal trainer to develop a periodized training plan that is appropriate for your goals and experience level.
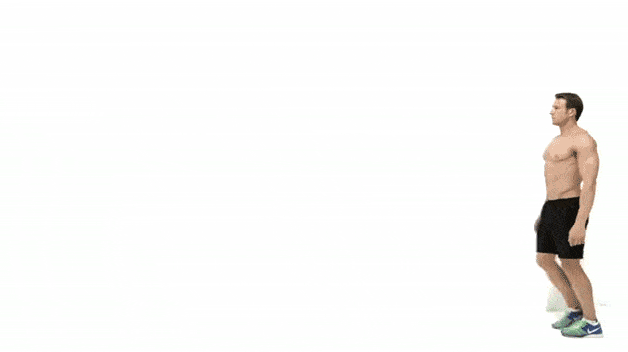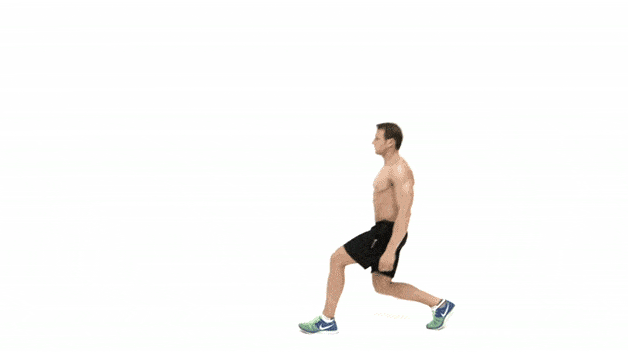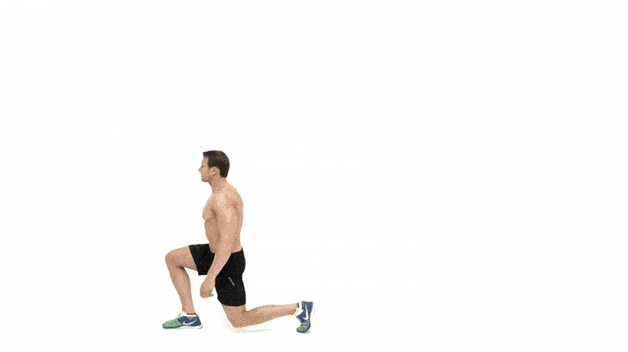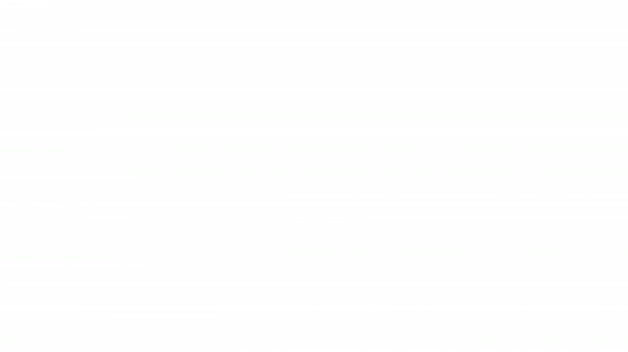
Basic movement drills and flexibility for beginners over 50
For beginners over 50, it is important to prioritize basic movement drills and flexibility exercises as part of their strength training routine. These exercises help to prepare the body for more intense strength training exercises, improve range of motion, prevent injuries, and promote overall mobility and functionality.
Preparing the body for strength training
Basic movement drills help to prepare the body for the demands of strength training exercises. This can include exercises such as bodyweight squats, lunges, push-ups, and planks, which target multiple muscle groups and mimic movements used in everyday life. These exercises help to activate and engage the muscles, improve coordination and balance, and warm up the joints.
Improving range of motion and preventing injuries
Flexibility exercises are essential for improving range of motion and preventing injuries in beginners over 50. By incorporating stretching exercises into their routine, such as static stretches or dynamic mobility exercises, individuals can improve their flexibility, reduce muscle stiffness and tightness, and increase joint mobility. This can help to prevent injuries caused by limited range of motion, such as muscle strains or joint sprains.
It is important to start with gentle and controlled movements, focusing on maintaining proper form and technique. Gradually increase the intensity and duration of the exercises as flexibility improves. It is also important to listen to your body and not push yourself beyond your limits, as this can increase the risk of injury.
Ten recommended exercises for men over 50
There are numerous exercises that can benefit men over 50, helping to improve strength, mobility, and overall fitness. Ten recommended exercises for men over 50 include:
-
Landmine shoulder press: This exercise targets the shoulders, triceps, and upper back muscles. It is performed by holding one end of a barbell or a landmine attachment with both hands and pressing it overhead.
-
Trap bar deadlifts: This exercise targets the glutes, hamstrings, and lower back muscles. It is performed by standing inside a trap bar and lifting it from the ground using a hip hinge movement.
-
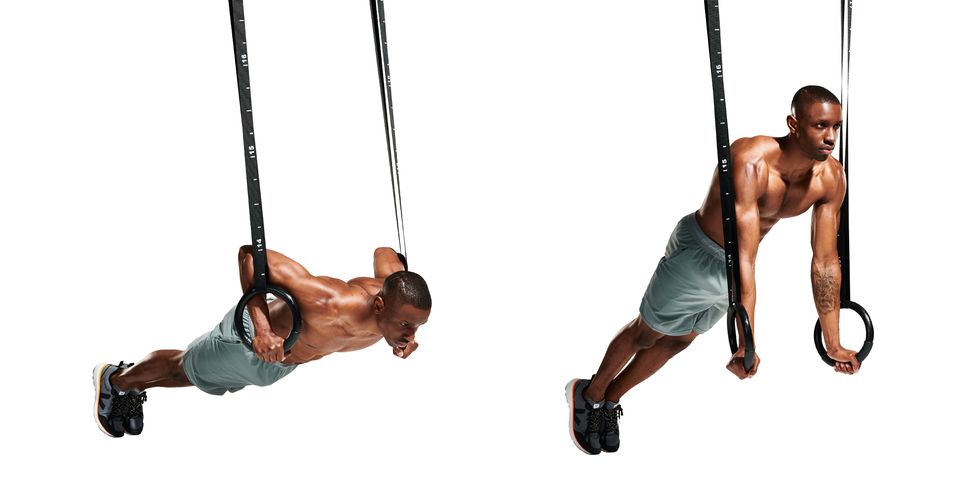
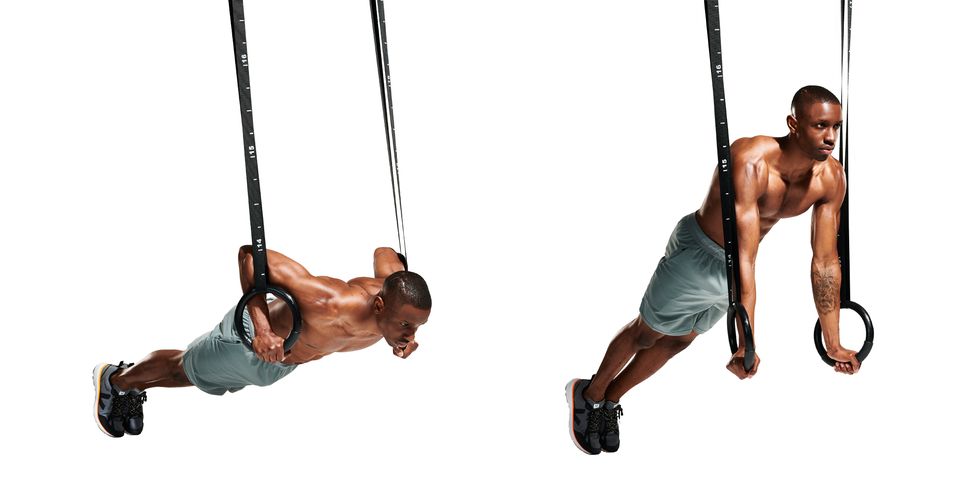
Gymnastic ring push-ups: This exercise targets the chest, shoulders, and triceps. It is performed by performing push-ups while gripping gymnastic rings, which adds an element of instability and engages more muscles for stabilization.
-
Walking lunges: This exercise targets the quadriceps, hamstrings, glutes, and calves. It is performed by taking a step forward, bending both knees to 90-degree angles, and then stepping forward with the opposite leg.
-
Chest supported rows: This exercise targets the muscles of the upper back, including the rhomboids, lats, and rear delts. It is performed by lying face down on an incline bench, gripping dumbbells or a barbell, and rowing the weight towards the chest.
-
Farmers carries: This exercise targets the muscles of the upper body, as well as the core and grip strength. It is performed by picking up heavy dumbbells or weight plates in each hand and walking for a set distance or time while maintaining good posture.
-
Goblet squats: This exercise targets the quadriceps, glutes, and core muscles. It is performed by holding a dumbbell or kettlebell at chest height, squatting down until your thighs are parallel to the ground, and then standing back up.
These exercises are just a few examples of the many options available for men over 50. It is important to choose exercises that are appropriate for your fitness level and goals, and to continuously challenge yourself as you progress. Working with a qualified fitness professional can help to ensure proper form and technique, as well as individualized exercise recommendations. Remember to always warm up before exercising, listen to your body, and prioritize safety and proper technique.









I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.